Researchers at Osaka University in Japan have developed an innovative flexible touchscreen interface. This cutting-edge technology allows the interface to flex and distort the content on the screen when you move your hand or fingers over the display. This unique feature not only adds a tactile dimension to touchscreen interactions but also enhances the user experience by providing more intuitive control over the displayed content.
How the Flexible Touchscreen Works
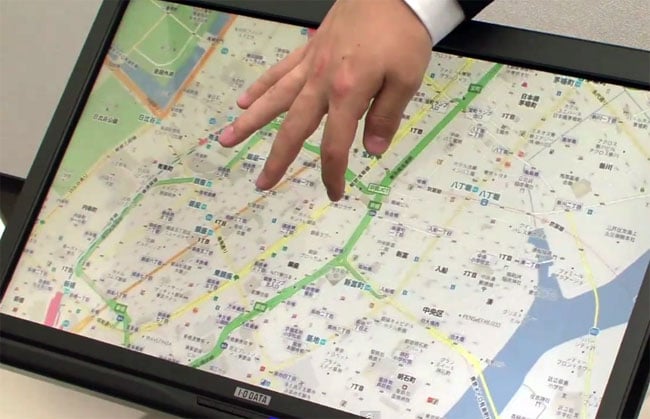
The flexible touchscreen interface developed by the researchers at Osaka University operates by detecting the pressure and movement of your fingers or hand over the display. When you apply pressure or move your fingers, the screen flexes, causing some of the content to become distorted. This distortion is not just a visual effect; it serves a functional purpose. By flexing the screen, users can scroll through content more efficiently and zoom into specific sections they want to examine more closely.
For example, imagine using this technology with a digital map application. As you move your fingers across the screen, the map flexes, allowing you to scroll through different areas quickly. When you find a region you want to explore in detail, you can apply more pressure to zoom in, making it easier to navigate and find specific locations. This method of interaction can be particularly useful for applications that require detailed examination of large datasets or images, such as architectural blueprints, medical imaging, or even gaming environments.
Applications and Benefits
The researchers tested this new touchscreen display technology with Google Maps, and the results were promising. The video below demonstrates how the flexible touchscreen interface works in practice, showcasing its potential to revolutionize the way we interact with digital maps and other applications.
The flexible touchscreen interface offers several advantages over traditional rigid touchscreens. Firstly, it provides a more immersive and interactive experience. The tactile feedback from the screen’s flexing can make digital interactions feel more natural and engaging. Secondly, the ability to distort and zoom into content seamlessly can enhance productivity, especially in professional fields that rely on detailed visual data.
For instance, in the field of education, this technology could be used to create interactive textbooks where students can zoom into diagrams and illustrations for a closer look. In the medical field, doctors could use flexible touchscreens to examine high-resolution medical images, such as X-rays or MRIs, with greater precision. Additionally, in the realm of entertainment, gamers could benefit from more dynamic and responsive controls, making gameplay more immersive.
It certainly looks very interesting in the video, and the way that more content can be displayed on the screen could make it really useful, especially for things like Google Maps. The potential applications of this technology are vast, and as it continues to develop, we can expect to see it integrated into various devices and platforms, enhancing the way we interact with digital content.
Source Crunch Gear, DigInfo
Latest Geeky Gadgets Deals
Disclosure: Some of our articles include affiliate links. If you buy something through one of these links, Geeky Gadgets may earn an affiliate commission. Learn about our Disclosure Policy.