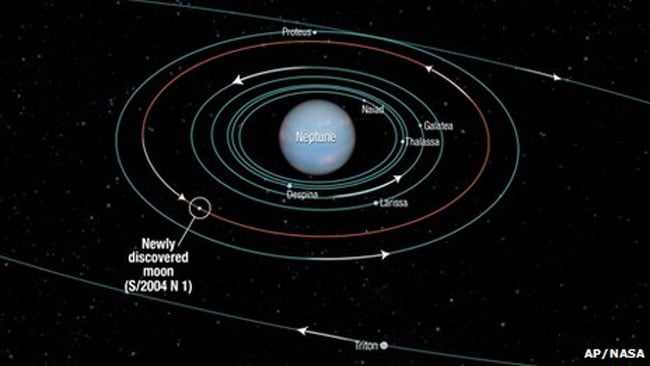
The Hubble Space Telescope has made a very interesting discovery having to do with Neptune. Hubble has discovered a new moon that was missed back in 1989 when Voyager flew past Neptune. The new moon was designated S/2004 N 1 and is the 14th known moon orbiting the planet.
Discovery of Neptune’s New Moon
The new moon also appears to be the smallest satellite orbiting Neptune at approximately 12 miles across. Scientists say that the moon completes one full orbit around Neptune every 23 hours. The moon was discovered by an American astronomer named Mark Showalter while he was studying segments of rings around the planet.
NASA says that the new moon is about 100 million times dimmer than the faintest star visible to the naked eye. The discovery was made by tracking the movement of a white fleck appearing over and over again in more than 150 photographs taken by Neptune between 2004 and 2009.
The discovery of S/2004 N 1 is particularly fascinating because it highlights the capabilities of the Hubble Space Telescope in detecting celestial objects that are incredibly faint and small. This moon is so dim that it was overlooked during the Voyager 2 flyby in 1989, which captured detailed images of Neptune and its moons. The fact that Hubble could identify such a tiny and faint object speaks volumes about the advancements in astronomical technology and techniques.
Significance of the Discovery
The discovery of this new moon adds to our understanding of the Neptunian system and the dynamics of its moons and rings. Each moon in the Neptunian system has its own unique characteristics and orbits, contributing to the complex gravitational interactions that shape the planet’s ring system. The presence of S/2004 N 1, despite its small size, could provide valuable insights into the formation and evolution of Neptune’s moons and rings.
Mark Showalter, the astronomer who discovered the moon, is known for his work on planetary rings and small moons. His discovery of S/2004 N 1 was made while he was analyzing the faint rings of Neptune, which are composed of dust particles and ice. The detection of the moon amidst these rings required meticulous examination of Hubble’s archival images, demonstrating the importance of thorough data analysis in astronomical research.
The discovery also raises questions about the potential for other small, undiscovered moons around Neptune and other planets in our solar system. As our observational technologies continue to improve, we may find more such moons, which could help us piece together the history and development of our solar system.
In addition to its scientific significance, the discovery of S/2004 N 1 has captured the public’s imagination. The idea that there are still unknown objects in our solar system waiting to be discovered is a reminder of the vastness and mystery of space. It underscores the importance of continued investment in space exploration and research, as each new discovery has the potential to expand our knowledge and understanding of the universe.
The discovery of Neptune’s 14th moon, S/2004 N 1, by the Hubble Space Telescope is a remarkable achievement that highlights the capabilities of modern astronomical technology. It adds to our understanding of the Neptunian system and raises intriguing questions about the potential for further discoveries in our solar system. As we continue to explore the cosmos, each new finding brings us one step closer to unraveling the mysteries of the universe.
via BBC
Latest Geeky Gadgets Deals
Disclosure: Some of our articles include affiliate links. If you buy something through one of these links, Geeky Gadgets may earn an affiliate commission. Learn about our Disclosure Policy.